Table of Contents
Toggle- Explore the main algorithms for sentiment analysis, including rule-based systems, traditional machine learning models, and advanced deep learning approaches, to understand how text classification is performed.
- Learn about various types of sentiment analysis such as fine-grained, aspect-based, and intent analysis, and their practical applications in business intelligence, customer feedback, and market research.
- Understand the challenges faced in sentiment analysis, including context interpretation, sarcasm detection, and the importance of high-quality training data to improve model accuracy and performance.
Understanding the Basics of Sentiment Analysis
Sentiment analysis, often called opinion mining, is the process of interpreting the emotional tone within written or spoken language. By applying natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning, a sentiment analysis model classifies text into positive, negative, or neutral categories. This capability helps organizations track how customers, employees, or the public feel about a product, brand, or issue.
The key benefit lies in transforming messy, unstructured language into structured intelligence. Platforms like ReputationPrime illustrate this power by automatically detecting shifts in customer sentiment, surfacing early complaints, and monitoring changes in reputation. Teams can complement this with Review Management Services to handle customer feedback at scale. Researchers apply similar methods to study political discourse or social issues, while businesses use them to evaluate product performance and service quality.
In today’s digital world—where millions of reviews, comments, and posts appear every day—manual analysis is impossible. Automated sentiment analysis ensures opinions are captured, categorized, and quantified at scale, providing real-time visibility into public attitudes.
Business Impact of Sentiment Analysis
Organizations receive feedback through support tickets, surveys, chat logs, and social media. Reviewing this information manually is slow, inconsistent, and resource-intensive. Sentiment analysis addresses these challenges by enabling companies to:
- Analyze millions of interactions in minutes.
- Detect emerging trends and risks early.
- Track product, brand, or service perception continuously.
The value extends beyond speed. Marketing teams can instantly adjust campaigns, service teams resolve high-risk cases, and executives gain a clear view of overall customer satisfaction. As a result, sentiment analysis becomes a cornerstone of modern customer intelligence and plays a vital role in managing online reputation.
Industry leaders stress that embedding sentiment analysis into daily decisions builds trust, strengthens loyalty, and delivers a lasting competitive advantage.

What Are Sentiment Analysis Models and Why Do They Matter?
At the core are algorithms that automatically classify sentiment. These range from simple lexicon-based rules to advanced deep learning architectures. The importance of these models lies in scalability. With millions of reviews and comments generated daily, algorithms offer:
- Rapid classification of massive datasets.
- Objective evaluations free from individual bias.
- Actionable insights that inform marketing, research, and product development.
This guide explores the main approaches—from rule-based systems to transformer models like BERT—so teams can choose the right method for their goals. Whether building a custom model or leveraging pre-trained systems, understanding algorithmic options is crucial when planning effective strategies and considering reputation management costs.

Approaches to determine sentiment: Key Concepts and Definitions
Core Algorithm Types
Rule-Based Systems
- Depend on dictionaries of positive and negative words and manually designed rules, often structured as clearly defined rules for interpreting sentiment.
- Use simple pattern-matching to determine polarity.
- Pro: Transparent and explainable.
- Con: Struggle with context, sarcasm, and evolving slang.
Traditional Machine Learning
- Require advanced AI architectures and manual feature extraction.
- Popular models: Naive Bayes, Logistic Regression, Support Vector Machines (SVMs).
- Pro: Scalable and interpretable.
- Con: Performance relies heavily on the quality of the data.
Deep Learning Algorithms
- Utilize artificial neural networks, such as RNNs, CNNs, and transformers (e.g., BERT).
- Automatically extract features from raw text inputs, thereby reducing the need for manual intervention.
- Pro: Capture complex human communication structures and context.
- Con: Demand vast supervised learning data, computing power, and tuning.
Hybrid Approaches
- Combine rule-driven sentiment analysis with ML or deep learning.
- Useful in domains requiring both transparency and precision.
Algorithm Dependencies and Workflow
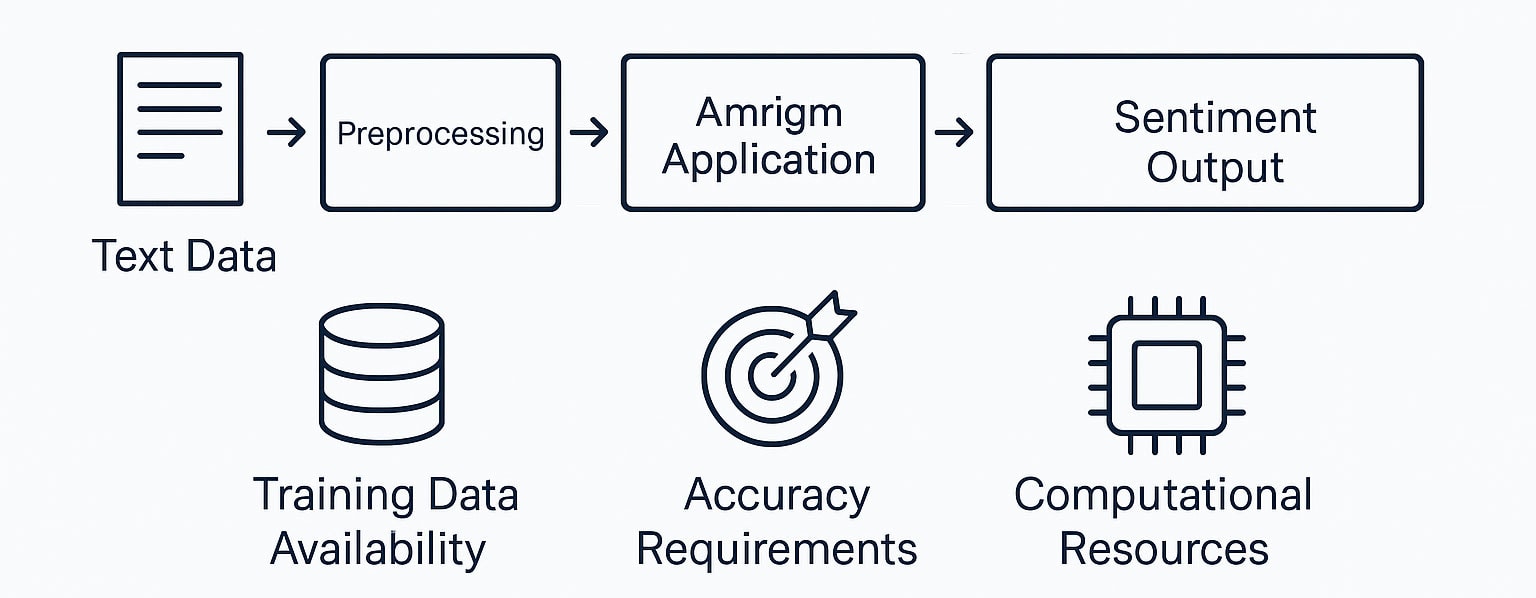
The general workflow follows:
Text Data → Preprocessing → Feature Extraction → Algorithm → Sentiment Output
- Preprocessing: Clean raw textual data by removing noise, normalizing text, and handling emojis.
- Feature Extraction: Convert text into TF-IDF, embeddings, or other numerical forms.
- Algorithm Application: Use classification algorithms to assign sentiment.
Choice depends on:
- Training Data: Rules suffice for limited data; neural-based learning systems excel with large, labeled training data.
- Accuracy Requirements: Simple models provide transparency, while advanced models achieve higher accuracy.
- Resources: Transformers require GPUs; lightweight models run on standard hardware.
Types of Sentiment Analysis
Different approaches allow analysis at varying depths:
- Polarity Classification: Categorizes text as positive, negative, or neutral.
- Fine Grained Sentiment Analysis: Distinguishes degrees of sentiment (e.g., slightly positive vs. very negative).
- Emotion Detection: Identifies emotions like joy, anger, or fear in textual communication.
- Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis (ABSA): Associates sentiment with specific features of products.
- Intent Analysis: Identifies goals behind statements (buying, canceling, complaining).
This progression advances from basic polarity detection to nuanced analysis, driving precise action.
Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis
ABSA is a powerful technique that provides deeper insights by associating sentiment categories with specific features. Instead of labeling an entire review as positive or negative, ABSA breaks it into components.
How ABSA Works
- Aspect Identification: Finds features (battery, price, staff).
- Sentiment Assignment: Attaches polarity to each feature.
- Model Training: Utilizes machine learning techniques, such as SVMs or AI-driven learning models, to classify.
Business Value of ABSA
- Granular Feedback: Identifies which features customers like or dislike.
- Targeted Improvements: Helps prioritize fixes or enhancements.
- Competitive Benchmarking: Compares aspect-level sentiment against rivals.
Industries like e-commerce, hospitality, automotive, and technology benefit significantly, as customers often evaluate multiple features within a single review.
Why Rule-Based Sentiment Analysis is Key to Business Intelligence
Organizations rely on sentiment classification to transform raw opinions into actionable insights. Benefits include:
Customer Experience
By analyzing support tickets, reviews, and businesses, one can:
- Detect dissatisfaction early.
- Respond rapidly to complaints.
- Personalize interactions based on sentiment scores.
This proactive approach strengthens loyalty and reduces churn.
Cost Reduction and Efficiency
Automated systems replace large manual teams. Where human reviewers might take weeks, algorithms deliver results in seconds. Companies save costs, accelerate responses, and scale analysis without expanding staff.
Real-Time Decision Making
Sentiment signals guide immediate actions:
- Service teams prioritize urgent cases.
- Marketing adjusts campaigns dynamically.
- Product teams spot feature-related issues faster.
In industries like finance, sentiment analysis work also supports predictive analytics, anticipating market reactions.

Competitive Intelligence
By monitoring conversations across online social networks, brands can benchmark their performance, identify unmet needs, and refine their messaging strategies more effectively than through traditional surveys, often leveraging advanced models, such as convolutional neural networks, to capture patterns in large-scale text data.
Market Research Innovation
Unlike surveys, sentiment analysis uncovers unfiltered, organic feedback. It highlights trends, detects intent (such as cancellations and upgrades), and reflects honest conversations in textual communication.

Applications of Sentiment Analysis
The practical value of artificial neural networks in sentiment analysis lies in their ability to transform unstructured text into insights that guide business strategy, product design, and policy-making. By leveraging machine learning methods for text classification and sentiment analysis, organizations that apply sentiment analysis effectively can uncover trends, anticipate risks, and respond to customer needs with greater precision. These machine learning methods ensure that insights are scalable and adaptable, making sentiment analysis impactful across industries. Below are the most common and actionable applications.
Customer Feedback Analysis
Every organization collects reviews, survey responses, and customer support tickets. Manually analyzing this volume is inefficient, while classification algorithms allow teams to rapidly identify negative sentiments, highlight recurring issues, and surface the factors driving positive sentiment. For example, a retailer may quickly detect growing dissatisfaction with delivery times while confirming that customers still value the quality of their products. Acting on these signals strengthens customer satisfaction and reduces churn.
Brand Monitoring
Reputation is shaped by what people say across online social networks, blogs, and review sites. Automated monitoring systems often rely on pre-labeled data and Sentiment Analysis to track overall sentiment, compare performance against competitors, and uncover market trends. A bank, for instance, might discover that customers praise its mobile app but criticize customer service. These insights, strengthened by models trained on pre-labeled data and enhanced through Sentiment Analysis, enable more targeted improvements and sharper competitive positioning. For individuals and businesses alike, effective brand monitoring can even extend to managing platforms like Reddit, where understanding sentiment and knowing how to delete Reddit accounts may become part of protecting digital reputation.
Social Media Monitoring
Social networks generate massive amounts of data daily. By combining predefined rules with sentiment analysis and AI-driven learning models, organizations can effectively interpret slang, hashtags, and emojis to uncover authentic, voiced sentiments online. Real-time monitoring enables the detection of viral crises, measures reactions to campaigns, and identifies emerging trends. For example, a brand launching a new product can instantly gauge whether the sentiment expressed skews positive, neutral, or negative, then adapt its messaging accordingly.

Product Development and Innovation
With Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis (ABSA), businesses uncover particular aspects of a product that generate praise or criticism. A technology company might find strong positive words around battery life, but consistent complaints about pricing. These insights guide product teams in refining roadmaps, prioritizing fixes, and allocating resources where they will have the most significant impact. This form of sentiment classification transforms raw feedback into a blueprint for innovation.
Specialized Use Cases
Beyond business, sentiment analysis supports specialized domains:
- Finance: Detect market signals from news sentiment to anticipate price shifts.
- Healthcare: Monitor patient feedback to improve care quality and reduce dissatisfaction.
- Government: Track citizen sentiment toward programs and policies for more responsive governance.
Together, these applications demonstrate how understanding sentiment enables organizations to make data-driven decisions, foster loyalty, and maintain a competitive edge.
Algorithm Performance Comparison Table
These algorithms are commonly used to predict sentiment in text data by assigning sentiment labels based on features extracted from the input.
This comparison illustrates that no single algorithm is “best” in all scenarios. Choices depend on:
- Data availability: Rule-based methods are suitable for low-data environments, while deep learning thrives on large datasets.
- Resource constraints: Traditional ML is efficient, while transformers demand heavy computing power.
- Business goals: Some applications require maximum accuracy (e.g., financial forecasting), while others prioritize speed and interpretability.
Scalability is another factor. Cloud APIs offer instant access to pre-trained models, while custom implementations provide greater control but require significant investment in infrastructure.
Challenges in Sentiment Analysis
- Despite progress, sentiment analysis challenges remain:
- Complexity of natural language, including sarcasm, irony, and the difficulty of correctly identifying neutral sentiment.
- Subjective interpretation of text.
- Scarcity or inconsistency in supervised learning data.
- Domain dependence—models trained in one area may misinterpret another, particularly when attempting to classify neutral sentiment.
- Rapidly evolving slang on social media platforms.
Overcoming these challenges requires domain adaptation, continuous retraining, and the use of advanced neural network models that can handle nuanced text.
Step-by-Step Guide to Implementing Sentiment Analysis Algorithms
Step 1: Data Preparation
- Clean text through tokenization, normalization, stop-word filtering, and emoji handling.
- Annotate consistently with reliable inter-annotator agreement.
Step 2: Algorithm Selection and Training
- Use rule-driven sentiment analysis for small datasets.
- Apply deep learning algorithms (BERT, LSTM) for higher accuracy.
- Cloud APIs provide fast deployment for teams with limited expertise.
Implementation examples using popular Python libraries:
# Traditional machine learning with scikit-learn
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
from sklearn.naive_bayes import MultinomialNB
from sklearn.svm import SVC
# Deep learning with Transformers
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForSequenceClassification
import torch
# Natural language processing with spaCy
import spacy
from spacytextblob.spacytextblob import SpacyTextBlobStep 3: Model Evaluation and Tuning
- Evaluate with metrics such as accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score.
- Address class imbalance with weighted loss or resampling.
- Apply cross-validation, ensembles, and retraining for robust performance.

Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Using generic models without customization can lead to the misinterpretation of domain-specific text.
- Relying on poor-quality or insufficient supervised learning data.
- Ignoring sarcasm, negation, and nuanced opinions expressed.
- Failing to preprocess slang, hashtags, or emojis from social media posts.
- Failing to monitor models can lead to drift over time.
Pro Tip: Start with pre-trained models and then fine-tune them with domain-specific data. This reduces effort while boosting accuracy.
Real-Life Example and Walkthrough
Case Study: TechGear Online
A mid-sized electronics retailer needed to manage 50,000+ monthly reviews. Manual review covered only 40% of the data, with an average response time of 14 days, leading to declining customer satisfaction.
By implementing an LSTM-based recurrent neural network, they achieved:
Results exceeded expectations across multiple metrics:
The results were transformative—2,000x faster processing, full coverage of reviews, and a 35% improvement in ratings. Faster responses also built trust, leading to higher loyalty and an 18% increase in revenue.
Best Practices for Implementing Sentiment Analysis
- Start with pre-trained deep learning algorithms and adapt them to your specific domain.
- Prioritize data quality over sheer volume.
- Monitor performance continuously to adapt to evolving human language.
- Integrate insights into decision-making rather than treating sentiment analysis as a standalone.
Turning Sentiment Analysis into a Strategic Advantage
The effective use of AI neural systems in sentiment analysis, ranging from rule-driven sentiment analysis to advanced deep learning, enables organizations to perform sentiment analysis accurately, connect polarity to specific aspects, and convert unstructured textual data into reliable insights. With sufficient labeled training data, advanced neural network models tuned for sentiment analysis, and thoughtful governance to limit unnecessary human intervention, teams can perform sentiment analysis at scale, supporting stronger conclusions and extracting meaningful patterns from the voiced sentiments.
By embedding these capabilities in customer feedback analysis, brand monitoring, product development, and research workflows, organizations create a durable advantage—lifting customer experience quality, reducing risk, and making smarter decisions across markets and channels. This systematic approach ensures that conclusion sentiment analysis provides actionable intelligence for both strategic planning and operational improvements, aligning closely with best practices for reputation repair online.
FAQs
Q1: Which algorithm works best for small datasets?
→ Rule-based systems or hybrid approaches work well. Pre-trained transformers can also be fine-tuned with as few as 100–500 labeled examples.
Q2: How do deep learning models handle sarcasm?
→ Context-aware models like BERT detect subtleties by analyzing word relationships. However, performance depends on having sarcastic examples in the supervised learning data.
Q3: What’s the difference between traditional ML and deep learning?
→ Traditional ML requires manual feature engineering and works well on small datasets. Deep learning methods, which utilize multiple layers, automatically learn patterns and achieve higher accuracy with large datasets.
Q4: How often should models be retrained?
→ At least quarterly, or whenever accuracy drops. Continuous monitoring ensures models stay relevant as human language evolves.
Q5: Can sentiment analysis handle multiple languages?
→ Yes. Models like mBERT support multilingual text, but results improve when fine-tuned on domain-specific data in the target language.

